• The ocean is the final repository of debris from the land.
• The ocean floor is almost covered with a blanket of sediments.
• The kinds of marine deposits differ a great deal from one part of the ocean to another.
Sources of marine deposits
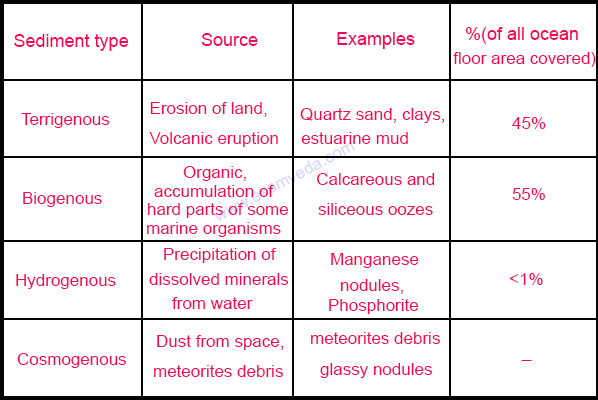
Types of deposits
The types of Ocean Deposits are Terrigenous materials and Biogenous materials.
Terrigenous materials
In general, the Terrigenous deposits consist mainly of &ndash
a) Material derived from the wear and tear of the land,
b) The remains of animals and plants,
c) Volcanic material.
• On the basis of size, composition and chemical characteristics, Terrigenous sediments are divided into gravels, sands, silt, clay and mud.
• Gravels are further sub-divided into boulders, cobbles, pebbles, granules etc in accordance with their size.
• Mud is finer than clay. Clay is significant cementing element.
Types of mud
Murray has divided mud into 3 types on the basis of colour.
Blue mud
• It includes the materials derived through the disintegration of rocks rich in Iron Sulphide and organic elements.
• It contains 35% of calcium carbonate.
• It predominates in the Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, Artic Sea.
Red mud
• The sediments derived through the communition of rocks rich in iron oxides from red mud.
• The reddish colour is mainly due to dominance of iron content.
• It predominates in the Yellow sea, Brazilian coast and the floors of Atlantic Ocean.
Green mud
• It is formed due to chemical weathering wherein the colour of blue mud is changed to green mud due to reaction of sea water.
• It contains green silicates of potassium and Glauconite.
• It contains calcium carbonate between 0 to 56%.
• These are generally found at the depth of 100 to 900 fathoms.
• Green mud are found along the Atlantic and Pacific coast of North America, Japan coast etc.
Biogenous materials
• The source of organic materials is sea itself. They include skeletons of marine organisms and plant remains. These are two categories
a) Neretic matter
b) Pelagic matter
• Neretic matter includes skeletons of marine organisms and plant remains.
• Pelagic matter consists of remains of different types of algae.
• Pelagic materials are oozes which are divided into two groups on the basis of lime and silica contents &ndash
I. Calcareous oozes &ndash
• They contain lime in abundance.
• They are seldom found at greater depth because of their high degree of solubility.
• They are generally found between the depths of 1000 fathoms to 2000 fathoms.
Pteropod oozes &ndash
• They are formed of floating pteropod mollusks.
• They contain 80% calcium carbonate and is mostly found in the tropical oceans and seas at the depth of 300 &ndash 1000 fathoms.
• They practically disappears beyond 2000 fathom depth.
Globigerina oozes &ndash
• They are formed from the shells of a variety of foraminifera but most of such oozes are formed of germs called globigerina.
• When they are dried up they become dirty white powder.
• They contain 64% calcium and 1.64% silica.
• They are found between the depths of 2000 to 4000 fathoms.
II. Siliceous oozes &ndash
• Silica content dominates in the siliceous oozes.
• Silica is derived from a group of protozoa or radiolarians and benthic animals mainly sponges.
• Such oozes are found in both warm and cold water at greater depths.
Radiolarian oozes &ndash
They are formed by the shell of radiolarian and foraminifera.
• They are found upto the depth of 2000 to 5000 fathoms.
Diatom oozes &ndash
• They are formed of the shells of very microscopic plants.
• They are found at the depth of 600 &ndash 2000 fathoms.
This article is shared by Priyanka Duta. Priyanka is a Guest Lecturer of Geography at New Alipore College, Kolkata.


Join The Discussion