51. In a triangle, if three altitudes are equal, then the triangle is
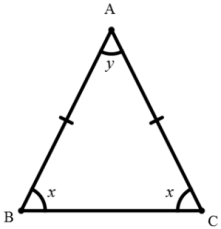
52. In an isosceles triangle, if the unequal angle is twice the sum of the equal angles, then each equal angle is
53. If the length of the sides of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : 5 : 6 and the inradius of the triangle is 3 cm, then the altitude of the triangle corresponding to the largest side as base is :
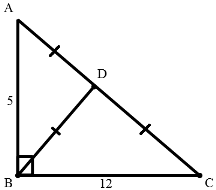
54. In a right-angle ΔABC, ∠ABC = 90°, AB = 5 cm and BC = 12 cm. The radius of the circumcircle of the triangle ABC is
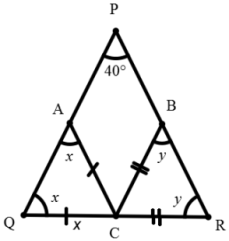
55. In triangle PQR, points A, B and C are taken on PQ, PR and QR respectively such that QC = AC and CR = CB. If ∠QPR = 40°, then ∠ACB is equal to:
56. If ABC is an equilateral triangle and D is a point of BC such that AD ⊥ BC, then
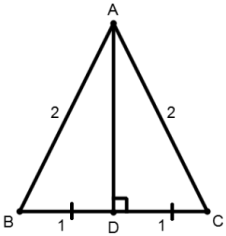
57. ΔABC is an isosceles triangle and $$\overline {AB} $$ = $$\overline {AC} $$ = 2a unit, $$\overline {BC} $$ = a unit. Draw $$\overline {AD} $$ ⊥ $$\overline {BC} $$ , and find the length of $$\overline {AD} $$
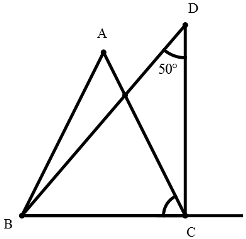
58. ABC is a triangle. The bisectors of the internal angle ∠B and external angle ∠C intersect at D. If ∠BDC = 50°, then ∠A is
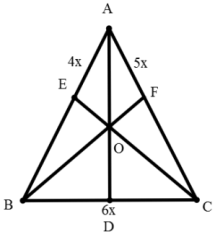
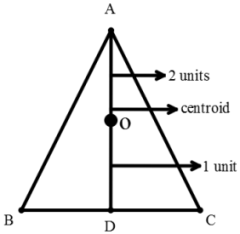
59. AD is the median of a triangle ABC and O is the centroid such that AO = 10 cm. The length of OD (in cm) is
60. The side QR of an equilateral triangle PQR is produced to the point S in such a way that QR = RS and P is joined to S. Then the measure of ∠PSR is
Read More Section(Triangles)
Each Section contains maximum 100 MCQs question on Triangles. To get more questions visit other sections.