12. Consider the Atomic Packing Factor (APF) of the following crystal structures:
P. Simple cubic
Q. Body centred cubic
R. Face centred cubic
T. Hexagonal close packed
Which two of the above structures have equal APF?
P. Simple cubic
Q. Body centred cubic
R. Face centred cubic
T. Hexagonal close packed
Which two of the above structures have equal APF?
13. If the number density of a free electron gas changes from 1028 to 1026 electron/m3, the value of plasma frequency (in Hz) changes from 5.7 × 1015 to
14. The dielectric constant of water is 80. However its refractive index is 1.75 invalidating the expression n = ε1/2. This is because
15. Density of states of free electrons in a solid moving with an energy 0.1 eV is given by 2.15 × 1021 e/V cm-3. The density of states (in e/V cm-3) for electrons moving with an energy of 0.4 eV will be
16. In a cubic system with cell edge a, two phonons with wave vectors $${\overrightarrow {\bf{q}} _1}$$ and $${\overrightarrow {\bf{q}} _2}$$ collide and produce a third phonon with a wave. vector $${\overrightarrow {\bf{q}} _3}$$ such that $${\overrightarrow {\bf{q}} _1} + {\overrightarrow {\bf{q}} _2} = {\overrightarrow {\bf{q}} _3} + \overrightarrow {\bf{R}} $$ where, $$\overrightarrow {\bf{R}} $$ is a lattice vector. Such a collision process will lead to
(a)
17. The point group symmetrics of the three molecules shown in figures are respectively
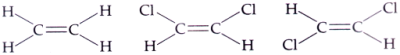
[Notation C2v = 2 mm; C2h = 2/m; D2h = mmm]

[Notation C2v = 2 mm; C2h = 2/m; D2h = mmm]
