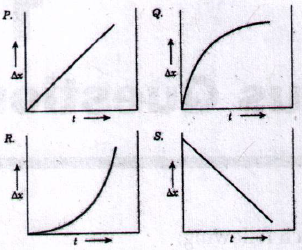
31. If 'Δx' represents adherent oxide layer thickness and 't' is time, which of the following curves represents diffusion controlled oxidation kinetics?

32. The reduction of FeO with CO gas in co-current flow is given by the following equation:
FeO + CO = Fe + CO2, ΔG° = 8120 J at 1173K The ratio of pco/pco2 for this reaction at 1173K is
FeO + CO = Fe + CO2, ΔG° = 8120 J at 1173K The ratio of pco/pco2 for this reaction at 1173K is
33. Zinc oxide is reduced at a constant temperature in a closed reactor using ZnO(s) and C(s) as the only starting materials. The following reactions are assumed to be at thermodynamic equilibrium:
ZnO(s) + C(s) = Zn(g) + CO(g)
2CO(g) = CO2(g) + C(s)
Assume ideal gas behaviour. Based on mole balance, the relationship applicable to the system at equilibrium is
ZnO(s) + C(s) = Zn(g) + CO(g)
2CO(g) = CO2(g) + C(s)
Assume ideal gas behaviour. Based on mole balance, the relationship applicable to the system at equilibrium is
34. For the irreversible reaction, Ca + C = CaC2, ΔH°298 = - 60,000 J.mol-1. If a system, initially containing 2 moles of calcium, 3 moles of carbon and one mole of calcium carbide, is allowed to react to completion, the heat evolved, at 298 K will be . . . . . . . . J.
35. The half-life period for second order reactions is given as
36. The expression for first law of thermodynamics
37. The effect of change in temperature on the entropy of formation of an ideal binary solution, ΔSM, id, is such that ΔSM, id
38. At absolute zero temperature, for any reaction involving condensed phases
39. In a binary system, the difference in chemical potentials of two components (μi - μj) is equal to
40. One mole of element P is mixed with one mole of element Q. The entropy of jnixing at 0°K is
Read More Section(Metallurgical Thermodynamics and Kinetics)
Each Section contains maximum 100 MCQs question on Metallurgical Thermodynamics and Kinetics. To get more questions visit other sections.
