A 20 B directional coupler is shown in the figure
The power output at port 3 will be
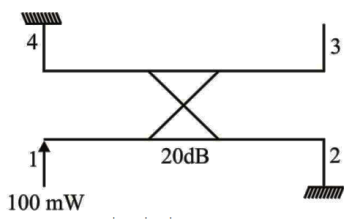
A. 10 mW
B. 1 mW
C. 5 mW
D. 2 mW
Answer: Option B

A. 10 mW
B. 1 mW
C. 5 mW
D. 2 mW
Answer: Option B
Coupling into and out of a traveling-wave tube can be accompanied by a
A. Waveguide match
B. Cavity match
C. Direct coax-helix match
D. All of the above
A. A long time constant
B. Low-pass filters
C. The shortest possible time
D. The restricted high-frequency response
A. $${\text{S}} = \frac{{2\lambda {\text{R}}}}{{\text{L}}}$$
B. $${\text{S}} = \frac{{3\lambda {\text{R}}}}{{\text{L}}}$$
C. $${\text{S}} = \frac{{\lambda {\text{R}}}}{{\text{L}}}$$
D. $${\text{S}} = \frac{{\text{L}}}{{\lambda {\text{R}}}}$$
The aquadag coating on the inside of PPI tube is used
A. To focus the beam of primary electrons
B. To shield the electron beam from unidirectional magnetic
C. As a second anode and to prevent the build-up of secondary field
D. All of these
Join The Discussion