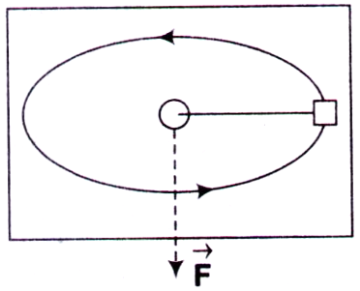
1. A mass m is constrained to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. It is set in circular motion with radius r0 and angular speed ω0 by an applied force $$\overrightarrow {\bf{F}} $$ communicated through an inextensible thread that passesthrough a hole on the surface as shown in figure given below. Then, this force is suddenly doubled.
The magnitude of the radial velocity of the mass

The magnitude of the radial velocity of the mass
