What is Insolation?
The radiant energy received from the sun, transmitted in a form analogous to shortwave (1/250 - 1/6700 mm in length), and travelling at the rate of 186000 miles a second is called solar radiation or Insolation. It is measured by the amount of solar energy received per square centimetre per minute.
The Fact on Sun
• The sun is supposed to have been formed of four major zones namely core, Photosphere, Chromospheres and Corona.
• The bright outer surface of the sun is called Photosphere because of the dominance of photons.
• The photosphere consists of 90 percent hydrogen and 10 percent helium.
• Within photosphere there are cool and dark spots, known as sunspots and hotspots which are collectively known as Faculae.
• The surface temperature of the sun is 60000 K.
The electromagnetic radiation emitted from the outer surface of the sun consists of four spectra of radiation waves :
a.The first spectrum of the electromagnetic waves includes gamma rays, hard X-rays, soft X-rays and ultra violet rays are called short waves.
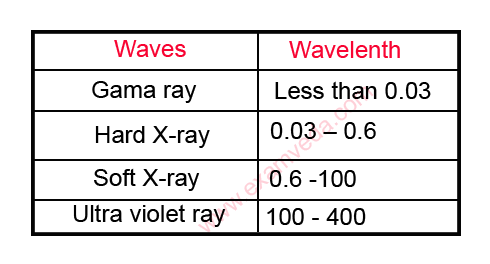
b. The second spectrum of the electromagnetic radiation waves is also called as the spectrum of visible light.
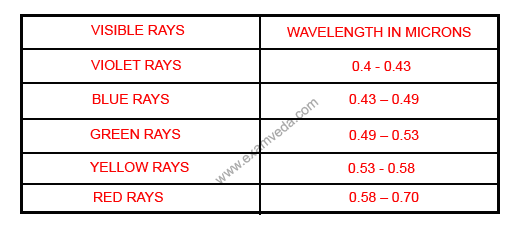
c. Third spectrum of the electromagnetic radiation waves is called as infrared spectrum which consists of infrared waves of the wavelengths ranging from 0.7 micron to 300 microns.
d. Fourth spectrum of the electromagnetic radiation waves consists of long waves including microwaves, radar waves and radio waves.
DISTRIBUTION OF INSOLATION
On an average, the amount of insolation received at the earth’s surface decreases from equator towards the poles but there is temporal variation of insolation received at different latitudes at different times of the year.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE DISTRIBUTION OF INSOLATION
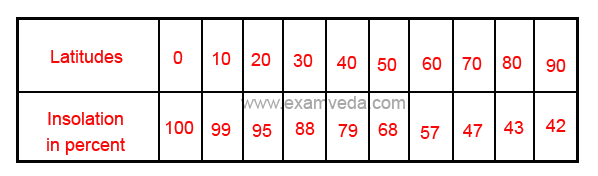
Angle of the sun’s ray
• As the angle of sun’s ray decrease poleward, the amount of insolation received also decreases in that direction.
• Vertical rays are spread over minimum area of the earth’s surface and they heat the minimum possible area and thus the energy received per unit area increases.
• Oblique rays are spread over larger area of the earth’s surface and hence the amount of energy received per unit area decreases.
• Oblique rays have to pass through thicker portion of the atmosphere than the vertical rays. thus the oblique rays have to travels larger distances than the vertical rays.
Length of day
• If all other conditions are favourable and equal then longer duration of sunshine and shorter duration of night enable the ground surface to receive larger amount of insolation.
Distance between the earth and the sun
• The earth at the time of perihelion (January 3), nearest to the sun, receive maximum insolation.
• While at the time of aphelion (July 4), farthest from the sun, receive minimum insolation.
Sunspots
• Sunspots defined as dark areas within photosphere of the sun and surrounded by chromospheres, are created in the solar surface.
• These dark areas are cool areas because they are characterized by 15000 c less temperature then the chromospheres which surrounded them.
• It is believed that the energy radiated from the sun increases when the number of sunspots increases and consequently the amount of insolation received at the earth’s surface also increases.
Effects of the atmosphere
• The incoming short wave solar radiation have to pass through a mean sun-earth distance of 149.5 million kilometers and the earth’s atmosphere and hence some portion of solar energy lost through the process of reflection, diffusion, absorption, scattering etc.
This article is shared by Priyanka Duta. Priyanka is a Guest Lecturer of Geography at New Alipore College, Kolkata.


Join The Discussion