
What is Air Mass?
An air mass may be defined as a large body of air whose physical properties, especially temperature, moisture content and lapse rate are more or less uniform horizontally for hundred kilometer.
• According to A.N.strahler and A.H.Strahler an air body in which the upward gradient of temperature and moisture are fairly uniform over a large area is known as an air mass.
Properties of an air mass determined by
I. The properties of the source area and the direction of its movement.
II. Changes introduced in the air mass during it’s journey way from the source area.
III. The age of the air mass.
• An air mass designated as cold air mass when it’s temperature is lower than underlying surface.
• While an air mass is termed warm air mass when it’s temperature is higher than the underlying surface.
• The boundary between two different air mass is called front.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE AIR MASSES
The following two characteristics of an air mass control the weather associated with it &ndash
• Vertical distribution of temperature in an air mass &ndashthe vertical distribution of temperature is indicative of the stability of an air mass beside it’s warmness and coldness.
• The moisture content of the air &ndashpresence or absence of condensation is determined by moisture content in the air mass.
SOURCE REGION OF THE AIR MASS
The extensive areas over which air masses originate or form are called source region, whose nature and properties largely determined the temperature and moisture characteristics of air masses.
An ideal source region of air mass must possesses the following essential conditions &ndash
• There must be extensive and homogenous earth surface so that it may possess uniform temperature and moisture conditions.
• Source region should be either land surface or ocean surface because irregular topography comprised both land and water cannot have uniform temperature and moisture condition.
• There should not be convergence of air rather there should be divergence of air flow so that the air may stay over the region for long period of time.
• Atmospheric conditions should be stable for considerable long period of time so that the air may attain the characteristics of the surface.
There are 6 major source regions of air masses &ndash
a. Polar oceanic areas
b. Polar and arctic continental area
c. Tropical oceanic areas
d. Tropical continental areas
e. Equatorial region
f. Monsoon areas of south east Asia.
TYPES OF AIR MASSES
On the basis of latitudinal position five types of air masses are distinguished as shown below -
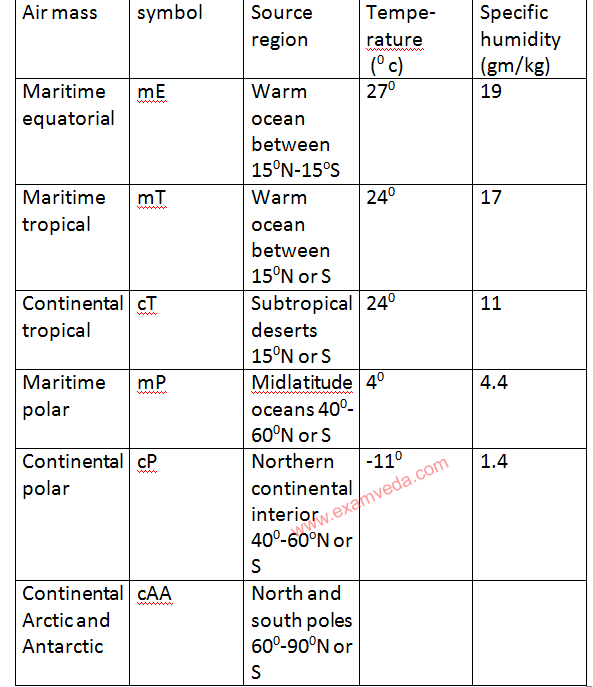
[ c = continent, m = maritime, P= polar, T= tropical, E=equatorial, A=arctic, AA=Antractic ]
Based on thermodynamics and mechanical modification and some other considerations air masses are divided into 16 types as follows-
A. Continental polar air masses(cP) &ndash
I. Continental polar cold stable air mass(cPKs)
II. Continental polar cold unstable air mass(cPKu)
III. Continental polar warm stable air mass(cPWs)
IV. Continental polar warm unstable air mass(cPWu)
B. Maritime polar air masses(mP) &ndash
I. Maritime polar cold stable air mass(mPKs)
II. Maritime polar cold unstable air mass(mPKu)
III. Maritime polar warm stable air mass(mPWs)
IV. Maritime polar warm unstable air mass(mPWu)
C. Continental tropical air masses (cT) &ndash
I. Continental tropical cold stable air mass(cTKs)
II. Continental tropical cold unstable air mass(cTKu)
III. Continental tropical warm stable air mass(cTWs)
IV. Continental tropical warm unstable air mass(cTWu)
D. Maritime tropical air masses(mT) &ndash
Maritime tropical cold stable air mass(mTKs)
II. Maritime polar cold unstable air mass(mTKu)
III. Maritime polar warm stable air mass(mPWs)
IV. Maritime polar warm unstable air mass(mPWu)
[K= cold, W=warm]
This article is shared by Priyanka Duta. Priyanka is a Guest Lecturer of Geography at New Alipore College, Kolkata.

Join The Discussion