In order to obtain a solution of the differential equation $$\frac{{{d^2}V}}{{d{t^2}}} - 2\frac{{dV}}{{dt}} + {V_1} = 0,$$ involving voltages V(t) and V1, an operational amplifier (op-amp) circuit would require at least
A. two op-amp integrators and one op-amp adder
B. two op-amp differentiators and one op-amp adder
C. one op-amp integrator and one op-amp adder
D. one op-amp integrator and one op-amp differentiator and one op-amp adder
Answer: Option A
A. is a common-emitter amplifier
B. uses a p-n-p transistor
C. is an oscillator
D. has a voltage gain less than one
A. 1 AND gate
B. 2 AND gates
C. 1 OR gate
D. 2 OR gates
A. the gain decreases by 10 times
B. the output resistance increases by 10 times
C. the fH increases by 100 times
D. the input resistance decreases by 100 times
The following circuit (where, RL ≫ R) performs the operation of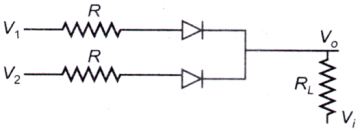
A. OR gate for a negative logic system
B. NAND gate for a negative logic system
C. AND gate for a positive logic system
D. AND gate for a negative logic system

Join The Discussion