1. A system has two energy levels with energies E and 2E. The lower level is four-fold degenerate while the upper level is doubly degenerate. If there are N non-interacting classical particles in the system, which is in thermodynamic equilibrium at temperature T, the fraction of particles in the upper level is
2. A system of non-interacting Fermi particles with Fermi energy EF has the density of states proportional to √E, where E is the energy of a particle. The average energy
per particle at temperature T = 0 is
3. A piston containing an ideal gas is originally in the state X (see figure). The gas is taken through a thermal cycle X → Y → X as shown
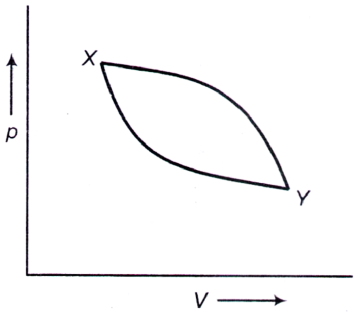
The work done by the gas is positive, if the direction of the thermal cycle is

The work done by the gas is positive, if the direction of the thermal cycle is
4. A photon gas is at thermal equilibrium at temperature T. The mean number of photons in an energy state $$\varepsilon = h\omega $$ is
5. In a classical micro-canonical ensemble for a system of N non-interacting particles, the fundamental volume in phase space which is regarded as equivalent to one micro-state is
(where, h is the Planck's constant.)
(where, h is the Planck's constant.)
